
-
 Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
Women sommeliers are cracking male-dominated wine world open
-
Exhibition of Franco-Chinese print master Zao Wou-Ki opens in Hong Kong

-
 Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
Myanmar junta denies killing civilians in hospital strike
-
Why SpaceX IPO plan is generating so much buzz

-
 Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
Thailand continues Cambodia strikes despite Trump truce calls
-
US envoy to meet Zelensky, Europe leaders in Berlin this weekend

-
 North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
North Korea acknowledges its troops cleared mines for Russia
-
US unseals warrant for tanker seized off Venezuelan coast

-
 Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
Cambodia says Thailand still bombing hours after Trump truce call
-
Machado urges pressure so Maduro understands 'he has to go'

-
 Best Gold Investment Companies in USA Announced (Augusta Precious Metals, Lear Capital, Robinhood IRA and More Ranked)
Best Gold Investment Companies in USA Announced (Augusta Precious Metals, Lear Capital, Robinhood IRA and More Ranked)
-
Leinster stutter before beating Leicester in Champions Cup

-
 World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks mostly slide, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Crypto firm Tether bids for Juventus, is quickly rebuffed

-
 Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
Union sink second-placed Leipzig to climb in Bundesliga
-
US Treasury lifts sanctions on Brazil Supreme Court justice

-
 UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
UK king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026
-
Wembanyama expected to return for Spurs in NBA Cup clash with Thunder

-
 Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
Five takeaways from Luigi Mangione evidence hearings
-
UK's king shares 'good news' that cancer treatment will be reduced in 2026

-
 Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
Steelers' Watt undergoes surgery to repair collapsed lung
-
Iran detains Nobel-prize winner in 'brutal' arrest

-
 NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
NBA Cup goes from 'outside the box' idea to smash hit
-
UK health service battles 'super flu' outbreak

-
 Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
Can Venezuela survive US targeting its oil tankers?
-
Democrats release new cache of Epstein photos

-
 Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
Colombia's ELN guerrillas place communities in lockdown citing Trump 'intervention' threats
-
'Don't use them': Tanning beds triple skin cancer risk, study finds
-
 Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
Nancy aims to restore Celtic faith with Scottish League Cup final win
-
Argentina fly-half Albornoz signs for Toulon until 2030

-
 Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes
Trump says Thailand, Cambodia have agreed to stop border clashes
-
Salah in Liverpool squad for Brighton after Slot talks - reports

-
 Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'
Marseille coach tips Greenwood as 'potential Ballon d'Or'
-
Draw marks 'starting gun' toward 2026 World Cup, Vancouver says

-
 Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce
Thai PM says asked Trump to press Cambodia on border truce
-
Salah admired from afar in his Egypt home village as club tensions swirl

-
 World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks retrench, consolidating Fed-fuelled gains
-
Brazil left calls protests over bid to cut Bolsonaro jail time

-
 Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies
Trump attack on Europe migration 'disaster' masks toughening policies
-
US plan sees Ukraine joining EU in 2027, official tells AFP

-
 'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears
'Chilling effect': Israel reforms raise press freedom fears
-
Iran frees child bride sentenced to death over husband's killing: activists

-
 No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure
No doubting Man City boss Guardiola's passion says Toure
-
Youthful La Rochelle name teen captain for Champions Cup match in South Africa

-
 World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains
World stocks consolidate Fed-fuelled gains
-
British 'Aga saga' author Joanna Trollope dies aged 82

-
 Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio
Man Utd sweat on Africa Cup of Nations trio
-
EU agrees three-euro small parcel tax to tackle China flood

-
 Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack
Taylor Swift breaks down in Eras documentary over Southport attack
-
Maresca 'relaxed' about Chelsea's rough patch


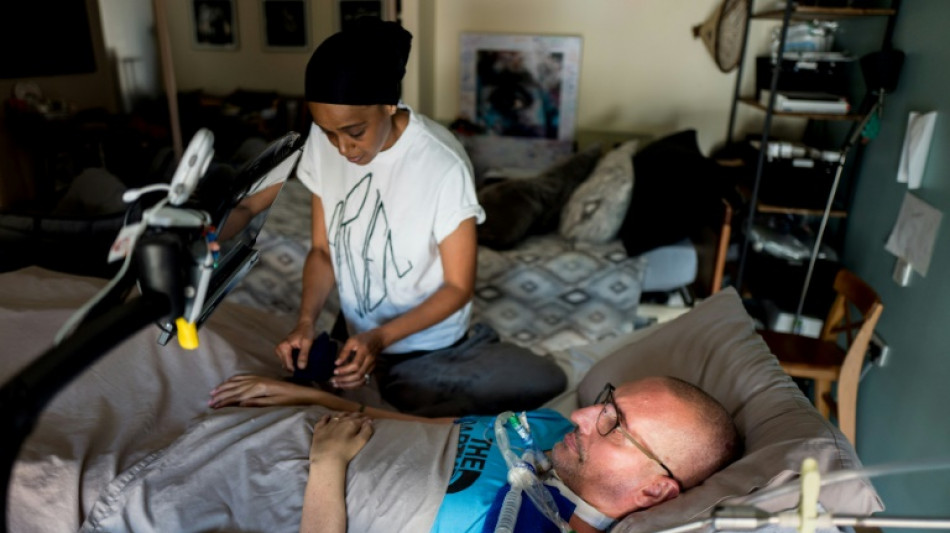
New treatment shows promise against fatal neurological disease: study
A new treatment shows promise against the deadly neurodegenerative disease ALS, a study based on mice showed Tuesday.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, sometimes called Lou Gehrig's disease after the famous baseball player, devastates nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord.
It affects about 30,000 Americans at any given time, causing progressive loss of motor and cognitive function. Most patients die within five years of their diagnosis.
In the new research, published in the journal PLOS Biology, a team led by Jeffrey Agar of Northeastern University investigated a way to target and stabilize an abundant enzyme that keeps cells safe from the toxic byproducts of consuming food and breathing oxygen.
Inherited mutations to the gene responsible for production of this protein, called SOD1, are involved in many cases of ALS, and at other times such mutations can occur without family history.
A malfunctioning SOD1 gene causes the protein to assemble into the wrong shape. This prevents it from doing its tasks, but can also trigger a build up of protein clumps that are also a hallmark of Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and other diseases.
Agar told AFP that over the course of 12 years, he and colleagues had discovered and tested a "molecular stabilizer," S-XL6, that acts like a "stitch" and forces the protein to remain in the correct configuration.
A major challenge involved finding a molecular stitch that would only target the SOD1, not "off target" proteins, which would poison the host.
The team tested their molecule in mice that were genetically modified to have a form of ALS disease, and found it not only restored the protein's function, but stopped its secondary toxic effects too. Safety was also proven in rats and dogs.
It successfully stabilized 90 percent of SOD1 proteins in blood cells, and 60-70 percent in brain cells.
They are hoping to soon get permission to move the molecule to clinical trials in humans, and an investor has purchased the rights to a patent.
Eventually, if it proves out, Agar said he hoped it might become a co-treatment for Biogen's Qalsody, a breakthrough regimen that received accelerated approval by the Food and Drug Administration in 2023, which works by reducing the number of SOD1 gene copies the body produces.
J.Oliveira--AMWN

