
-
 Google must open Android to rival app stores: US court
Google must open Android to rival app stores: US court
-
Amazon profits surge 35% as AI investments drive growth

-
 Zelensky urges allies to seek 'regime change' in Russia
Zelensky urges allies to seek 'regime change' in Russia
-
Trump envoy to inspect Gaza aid as pressure mounts on Israel

-
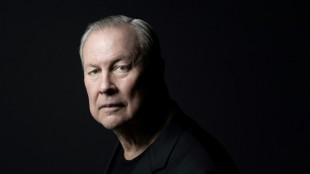 US theater and opera legend Robert Wilson dead at 83
US theater and opera legend Robert Wilson dead at 83
-
EA shooter 'Battlefield 6' to appear in October

-
 Heavyweight shooter 'Battlefield 6' to appear in October
Heavyweight shooter 'Battlefield 6' to appear in October
-
Justin Timberlake says he has Lyme disease

-
 Atkinson and Tongue strike as India struggle in England decider
Atkinson and Tongue strike as India struggle in England decider
-
US theater and opera auteur Bob Wilson dead at 83
-
 Trump envoy to visit Gaza as pressure mounts on Israel
Trump envoy to visit Gaza as pressure mounts on Israel
-
In Darwin's wake: Two-year global conservation voyage sparks hope

-
 Microsoft valuation surges above $4 trillion as AI lifts stocks
Microsoft valuation surges above $4 trillion as AI lifts stocks
-
Verstappen quells speculation by committing to Red Bull for 2026

-
 Study reveals potato's secret tomato past
Study reveals potato's secret tomato past
-
Trump's envoy in Israel as Gaza criticism mounts

-
 Squiban solos to Tour de France stage win, Le Court maintains lead
Squiban solos to Tour de France stage win, Le Court maintains lead
-
Max Verstappen confirms he is staying at Red Bull next year

-
 Mitchell keeps New Zealand on top against Zimbabwe
Mitchell keeps New Zealand on top against Zimbabwe
-
Vasseur signs new contract as Ferrari team principal

-
 French cities impose curfews for teens to curb crime
French cities impose curfews for teens to curb crime
-
Seals sing 'otherworldly' songs structured like nursery rhymes

-
 India captain Gill run out in sight of Gavaskar record
India captain Gill run out in sight of Gavaskar record
-
Trump's global trade policy faces test, hours from tariff deadline

-
 Study reveals potato's secret tomato heritage
Study reveals potato's secret tomato heritage
-
Wirtz said I would 'enjoy' Bayern move, says Diaz

-
 West Ham's Paqueta cleared of betting charges
West Ham's Paqueta cleared of betting charges
-
AI gives stocks a lift, dollar mixed tracking Fed, tariffs

-
 Authorities abandon recovery of German Olympian killed in Pakistan
Authorities abandon recovery of German Olympian killed in Pakistan
-
Talks over France, Lions game 'progressing': Benazzi

-
 Popovici ready to hit the beach after world swim sprint double
Popovici ready to hit the beach after world swim sprint double
-
Magic Marchand adds gold to world record as McIntosh wins again

-
 Sweden jihadist jailed for life over Jordan pilot burned alive
Sweden jihadist jailed for life over Jordan pilot burned alive
-
Zelensky signs bill ensuring anti-graft agencies' 'independence'

-
 Sleepless in Singapore: Marchand wins gold, day after world record
Sleepless in Singapore: Marchand wins gold, day after world record
-
England make early double strike in India series decider

-
 Popovici wins 100m freestyle world gold for sprint double
Popovici wins 100m freestyle world gold for sprint double
-
Marchand wins 200m medley gold, day after world record

-
 Thousands of Afghans scramble for chance to work in Qatar
Thousands of Afghans scramble for chance to work in Qatar
-
Trump's envoy arrives in Israel as Gaza criticism mounts

-
 McIntosh powers to third gold of worlds, 12-year-old Yu fourth
McIntosh powers to third gold of worlds, 12-year-old Yu fourth
-
Hong Kong sees 3.1% growth in second quarter

-
 Stocks, dollar mixed tracking Fed, tariffs, results
Stocks, dollar mixed tracking Fed, tariffs, results
-
World Athletics brings in gene tests for female category eligibility

-
 Trump says tariffs are making US 'great & rich' again
Trump says tariffs are making US 'great & rich' again
-
Pakistan opposition leader given 10 years for Imran Khan protests

-
 India's Bumrah out of Oval finale as England bowl in fifth Test
India's Bumrah out of Oval finale as England bowl in fifth Test
-
Rights groups urge Nepal to reverse Telegram ban

-
 BMW says can weather tariff storm despite profit plunge
BMW says can weather tariff storm despite profit plunge
-
Zelensky urges allies to push for 'regime change' in Russia

| SCU | 0% | 12.72 | $ | |
| RBGPF | 0.52% | 74.42 | $ | |
| RYCEF | 7.62% | 14.18 | $ | |
| CMSC | 1.09% | 22.85 | $ | |
| BCC | -1.29% | 83.81 | $ | |
| NGG | 0.28% | 70.39 | $ | |
| BCE | -0.86% | 23.33 | $ | |
| CMSD | 0.9% | 23.27 | $ | |
| RIO | 0.47% | 59.77 | $ | |
| SCS | 0% | 10.33 | $ | |
| JRI | 0.15% | 13.13 | $ | |
| RELX | 0.21% | 51.89 | $ | |
| VOD | -2.31% | 10.81 | $ | |
| AZN | -4.79% | 73.09 | $ | |
| BTI | 0.97% | 53.68 | $ | |
| GSK | -4.9% | 37.15 | $ | |
| BP | -0.31% | 32.15 | $ |

EU ministers mull climate policy, carbon border tax
European Union environment ministers gathered in France Thursday to mull climate policy and the merits of a carbon border tax, while airing differences on whether nuclear energy can be classified as "green".
The two-day informal talks in Amiens, hosted by France as it takes the rotating reins of the EU presidency, will look for a unified path toward achieving the 27-nation bloc's ambitious target of slashing carbon emissions 55 percent from 1990 levels.
Discussion on overhauling the EU's electricity market and carbon-trading system, already fraught, unfolds against a backdrop of sharp increases in energy prices, especially natural gas.
EU energy ministers will join the fray on Friday, and then continue on with separate talks.
Since last year, French President Emmanuel Macron has led the charge for the rapid implementation of a "carbon border adjustment mechanism", essentially a tax on imported products made in countries with less stringent rules on reducing carbon pollution.
The objective is to avoid shifting Europe's carbon emissions overseas as they are reduced at home -- known as "carbon leakage".
The sectors affected include steel, alumium, cement, fertiliser and electricity.
China and the United States are both opposed to such a tax, with Beijing saying last year when the plan was unveiled that it would "violate World Trade Organization (WTO) principles."
- Is nuclear 'green'? -
Even within Europe, Germany insists the mechanism can only be implemented gradually, and several countries are outright opposed, mainly because the tax would replace the allocation of free emissions permits.
"Spain, Portugal, Poland and Austria want to maintain free quotas," a European diplomat said.
Such a carbon tax "raises complicated questions," he added. "Who collects the money? Where does it go?"
But France's ecological transition minister Barbara Pompili said that there is already an "agreement in principle", and talks have shifted to questions of timing.
After EU ministers hammer out a consensus on "CBAM", as it is known, they will undertake negotiations with the EU Parliament to finalise an agreement.
Another divisive issue that has pitted Paris against Berlin is whether nuclear power's virtue as a source of carbon-free energy outweighs safety issues and the as-yet unsolved problem of nuclear waste.
A greater share of electricity in France -- about 70 percent -- is generated by nuclear power than any other country in the world.
The question on the table is whether nuclear power and natural gas should be officially classified in the "EU taxonomy" as environmentally sustainable, an important signal to companies, investors and policymakers.
Nuclear power is neither "sustainable" nor "economic", Germany environment minister Stefan Tidow said in Amiens. "It is not a green energy."
Pompili did not disagree, acknowledging that storage of spent nuclear fuel remains a major problem.
- 'Imported deforestation' -
But "nuclear is a decarbonised energy," she said. "We cannot deprive ourselves of it at the same time that we need to very rapidly reduce our carbon emissions."
A third initiative favoured by France is developing tools to fight so-called "imported deforestation," stemming from products indirectly responsible for the destruction of tropical forests.
Palm oil plantations in Southeast Asia and Africa, and commercial soy production in South America -- mostly to feed cattle -- are major drivers of deforestation.
A draft law submitted by the European Commission in November is currently under discussion in the bloc's Parliament.
Environmental NGOs said the text has too many loopholes, excluding commodities such as corn and rubber.
Yet another initiative running into stiff headwinds is a measure to expand the cap-and-trade system of carbon pollution quotas -- which currently covers heavy industry and the electricity sector -- to transport fuel for trucks and domestic heating fuel.
The controversial proposal, championed by the European Commission, has found scant support among ministers, concerned the measure would result in unpopular price hikes for consumers.
France has expressed "strong reservations," according to a French official.
"We saw the rise of the 'yellow vests'," he said, referring to popular protests in 2018 sparked by a modest increase in petrol prices.
Ch.Havering--AMWN