
-
 Stokes prefers media heat in Australia to 'miserable, cold' England
Stokes prefers media heat in Australia to 'miserable, cold' England
-
Italy's luxury brands shaken by sweatshop probes

-
 France's Macron visits China with Ukraine on the agenda
France's Macron visits China with Ukraine on the agenda
-
In Data Center Alley, AI sows building boom, doubts

-
 Women don fake mustaches in LinkedIn 'gender bias' fight
Women don fake mustaches in LinkedIn 'gender bias' fight
-
Doctor to be sentenced for supplying Matthew Perry with ketamine

-
 Football world braces for 2026 World Cup draw with Trump presiding
Football world braces for 2026 World Cup draw with Trump presiding
-
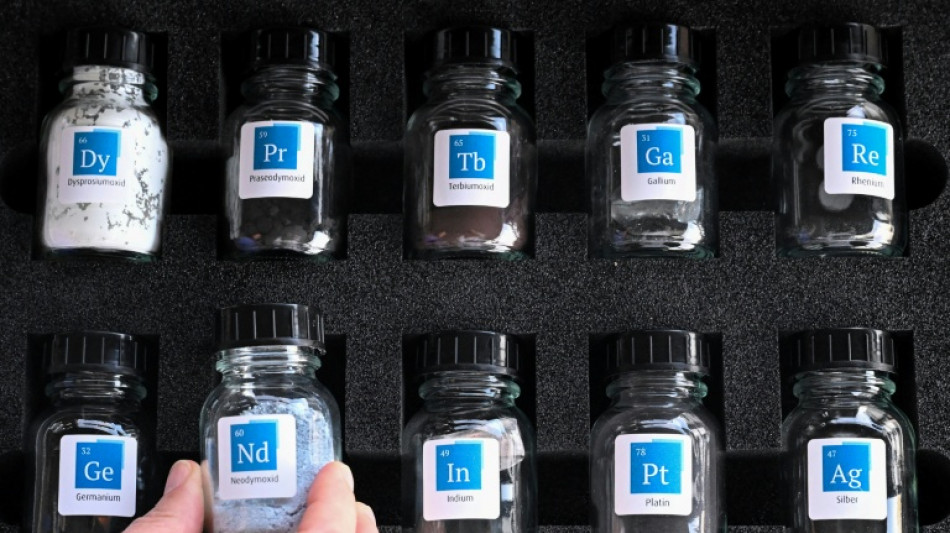
What are 'rare earths' for?

-
 Honduran ex-president leaves US prison after Trump pardons drug crimes
Honduran ex-president leaves US prison after Trump pardons drug crimes
-
Chanderpaul, Hope see West Indies to 68-2 after New Zealand's 231

-
 YouTube says children to be 'less safe' under Australia social media ban
YouTube says children to be 'less safe' under Australia social media ban
-
Polarised South Korea marks martial law anniversary

-
 US, Russia find 'no compromise' on key territory issue after Ukraine talks
US, Russia find 'no compromise' on key territory issue after Ukraine talks
-
Family voices new alarm for Hong Kong's jailed Jimmy Lai

-
 San Francisco sues producers over ultra-processed food
San Francisco sues producers over ultra-processed food
-
Honduras' Hernandez: Convicted drug trafficker pardoned by Trump

-
 Romero bicycle kick rescues point for Spurs against Newcastle
Romero bicycle kick rescues point for Spurs against Newcastle
-
Barca make Atletico comeback to extend Liga lead

-
 Leverkusen knock Dortmund out of German Cup
Leverkusen knock Dortmund out of German Cup
-
Steve Witkoff, neophyte diplomat turned Trump's global fixer

-
 Man City's Haaland makes 'huge' Premier League history with 100th goal
Man City's Haaland makes 'huge' Premier League history with 100th goal
-
Sabrina Carpenter condemns 'evil' use of her music in White House video

-
 Tech boss Dell gives $6.25bn to 'Trump accounts' for kids
Tech boss Dell gives $6.25bn to 'Trump accounts' for kids
-
Trump hints economic adviser Hassett may be Fed chair pick

-
 US stocks resume upward climb despite lingering valuation worries
US stocks resume upward climb despite lingering valuation worries
-
Haaland century makes Premier League history in Man City's nine-goal thriller

-
 Serena Williams denies she plans tennis return despite registering for drug tests
Serena Williams denies she plans tennis return despite registering for drug tests
-
Defense challenge evidence in killing of US health insurance CEO

-
 Man City's Haaland makes Premier League history with 100th goal
Man City's Haaland makes Premier League history with 100th goal
-
Putin and US negotiators hold high-stakes Ukraine talks in Moscow

-
 Spain overpower Germany to win second women's Nations League
Spain overpower Germany to win second women's Nations League
-
'HIV-free generations': prevention drug rollout brings hope to South Africa
-
 US medical agency will scale back testing on monkeys
US medical agency will scale back testing on monkeys
-
Faberge's rare Winter Egg fetches record £22.9 mn at auction

-
 Snooker great O'Sullivan loses to Zhou in UK Championship first round
Snooker great O'Sullivan loses to Zhou in UK Championship first round
-
Pentagon chief says US has 'only just begun' striking alleged drug boats

-
 Putin receives top US negotiators in high-stakes Ukraine talks
Putin receives top US negotiators in high-stakes Ukraine talks
-
Under Trump pressure, Honduras vows accurate vote count

-
 O'Neill salutes Celtic players for 'terrific' response
O'Neill salutes Celtic players for 'terrific' response
-
Pope urges halt to attacks in Lebanon as first voyage abroad ends

-
 Amazon unveils new AI chip in battle against Nvidia
Amazon unveils new AI chip in battle against Nvidia
-
Pope plans trip to Africa, starting with Algeria

-
 Woods recovery 'not as fast as I'd like', no timetable for return
Woods recovery 'not as fast as I'd like', no timetable for return
-
'Come and kill me': sick ants invite destruction to save colony

-
 Red Bull promote rookie Hadjar to partner Verstappen
Red Bull promote rookie Hadjar to partner Verstappen
-
Zelensky calls for peace, Putin defiant ahead of US-Russia talks

-
 Mbappe more than his goals: Real Madrid coach Alonso
Mbappe more than his goals: Real Madrid coach Alonso
-
Sport court allows Russian, Belarusian skiers to qualify for Olympics

-
 Cyclone turns Sri Lanka's tea mountains into death valley
Cyclone turns Sri Lanka's tea mountains into death valley
-
IOC president calls for end to 'finger-pointing' in doping fight


What are 'rare earths' for?
Crucial for making smartphones, fighter jets and electric cars, "rare earth" metals have become a strategic bargaining chip since main producer China this year introduced restrictions on their exports.
As the EU unveils a plan on Wednesday for boosting European production of critical raw materials to reduce reliance on China, here are some facts about these 17 elements and their key uses:
- Neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium, terbium -
Global raw production of rare earths increased from 220,000 tonnes in 2019 to 390,000 tonnes in 2024 -- an increase of 77 percent over five years, according to a benchmark commodities report by French research group Cercle CyclOpe.
Four elements account for most of the sector's economic value: neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and terbium.
- Magnets for wind turbines -
These four "magnetic" rare earths are mainly used to make magnets, notably neodymium-iron-boron magnets -- about 10 times more powerful than conventional ones.
Use of the rare elements maximises magnets' performance while reducing size and weight, said Damien Ambroise, energy manager at French consultancy Bartle.
A single offshore wind turbine contains up to one tonne of such magnetic rare earths.
- Fighter jets, golf clubs -
Aviation is a major consumer of rare earths, especially for military plane manufacturing.
According to the US specialist newsletter Rare Earth Exchanges, US aerospace firm Lockheed Martin is the biggest American user of samarium, employed to make magnets that can withstand extremely high temperatures.
Each F-35 fighter jet requires more than 400 kilograms of rare earths, according to a report by the US Congressional Research Service.
Scandium is used to make light, strong aluminium-based alloys prized in aerospace -- and also in high-end sports gear such as golf clubs, bicycles and baseball bats.
- Smartphones -
Rare earths are also found in every smartphone, enhancing screen performance and enabling the phone to vibrate.
Each handset contains about three grams of them -- more than 3,700 tonnes overall for the 1.24 billion devices sold worldwide in 2024.
- Electric and fuel vehicles -
Each hybrid or electric vehicle battery and motor contains between 1.2 and 3.5 kilograms of rare earths, according to an estimate by France's Bureau of Geological and Mining Research.
They are also used in the manufacture of miniature motors, such as those that fold away a car's wing mirrors automatically when it is parked.
Combustion-engine vehicles use rare earths too, notably in catalytic converters. Lanthanum and cerium help cut fine particle emissions.
- Oil, glass, lasers -
In the chemical industry, cerium is widely used in oil refining and glass polishing -- as well as in flints for cigarette lighters.
Erbium is used in various medical fields, including dentistry, dermatology and ophthalmology.
Erbium and neodymium are also important in making lasers for industrial engraving and cutting.
Adding different rare earths alters the wavelength of the laser, and thus its use and colour, Ambroise said. "It makes for pretty colours in sound-and-light shows."
S.F.Warren--AMWN