
-
 'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
'One Battle After Another' location manager explains THAT car chase
-
Why have 1,000 ships at times lost their GPS in the Mideast?

-
 Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
Djokovic battles back to win Indian Wells opener
-
Thompson strike seals US victory in SheBelieves Cup

-
 Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
Berger's lead narrows at rain-hit Arnold Palmer
-
Netanyahu vows to press Iran war as Trump honors slain US troops

-
 Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
Messi bags 899th goal as Miami down DC United
-
Turkey warns over 'dangerous' bid to stir civil war in Iran

-
 Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
Yamal bends Barca past Bilbao, Atletico edge Real Sociedad
-
Marseille take revenge on Toulouse and rise to third in Ligue 1

-
 New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
New attacks in Gulf as Iran vows for more
-
Yamal class secures Barca narrow win at Athletic Bilbao

-
 Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
Man City hand Newcastle brutal FA Cup lesson as Chelsea survive scare
-
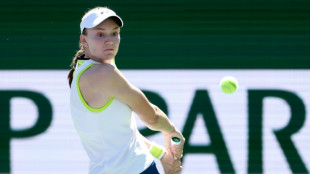
Rybakina holds off Baptiste in testing Indian Wells opener
-
 Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
Como boost Champions League bid, Juve back to winning ways
-
As Iran conflict spills over, Iraq's Kurds say 'this war is not mine'

-
 Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
Protests across globe mark one week of Iran war
-
US starts using UK bases for 'defensive' Iran operations

-
 Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
Chelsea deny 10-man Wrexham Hollywood finish in FA Cup thriller
-
Netanyahu vows to carry on war, 'eradicate Iranian regime'

-
 Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
Gonzalez brace helps Atletico beat Real Sociedad
-
Dortmund beat 10-man Cologne to tighten grip on top-four spot

-
 'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
'We've given ourselves an opportunity', says Tuipulotu after win over France
-
Skiing 'filled the void' for Paralympian Soens after life-changing fall

-
 Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
Lamaro praises Italy's history-making 'wall in defence'
-
Italy make history in Six Nations beating England for first time

-
 Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
Tehran residents keep up semblance of normality amid destruction
-
Griezmann 'will continue' with Atletico despite MLS option: sporting director

-
 Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
Protesters come out for Iran, against war in spots across the globe
-
Scotland throw open Six Nations title race with stunning win over France

-
 Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
Leverkusen held at Freiburg before Arsenal clash
-
Trump offers LatAm leaders US missile strikes to hit drug cartels

-
 Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
Key to Scotland win over France was fast start, says Steyn
-
Iran fires at Gulf neighbours as Trump threatens more strikes

-
 Scotland stun France 50-40 to take Six Nations to wire
Scotland stun France 50-40 to take Six Nations to wire
-
Pogacar begins season with dominant Strade Bianche win

-
 Failed Israeli commando operation to find airman remains kills 41 in Lebanon
Failed Israeli commando operation to find airman remains kills 41 in Lebanon
-
Bronze and Stanway on target for England in World Cup qualifying

-
 'No pressure, no fun', says India's Suryakumar ahead of World Cup final
'No pressure, no fun', says India's Suryakumar ahead of World Cup final
-
Russian strikes kill 12 across Ukraine

-
 Women rule the roost atop the Gdansk shipyard cranes
Women rule the roost atop the Gdansk shipyard cranes
-
'Fun day' for Olympic champion Braathen in giant slalom win

-
 Bayern's Neuer out of Atalanta tie with calf tear
Bayern's Neuer out of Atalanta tie with calf tear
-
Arsenal survive FA Cup scare to keep quadruple dream alive

-
 Ohtani homers again as Japan edge South Korea at World Baseball Classic
Ohtani homers again as Japan edge South Korea at World Baseball Classic
-
Japan hammer India 11-0 in Women's Asian Cup mismatch

-
 Trump threatens to escalate bombing as Iran vows no surrender
Trump threatens to escalate bombing as Iran vows no surrender
-
Russian strikes kill 11 across Ukraine

-
 Nepal's rapper politician who took on the old guard and won
Nepal's rapper politician who took on the old guard and won
-
Pirovano doubles up with second Val di Fassa downhill win


Methane rising faster than other greenhouse gases: researchers
Concentrations in the atmosphere of the powerful greenhouse gas methane are rising at an accelerating pace, threatening efforts by countries to meet their climate targets, researchers warned on Tuesday.
"Methane is rising faster in relative terms than any major greenhouse gas and is now 2.6-fold higher than in pre-industrial times," said an international group of researchers under the aegis of the Global Carbon Project in a study published in Environmental Research Letters.
Methane is the second most abundant greenhouse gas produced by human activity after carbon dioxide, with agriculture, energy production and organic waste rotting in landfills the major sources.
In the first 20 years, its impact on the atmosphere is about 80 times more powerful that of carbon dioxide but it breaks down more quickly than CO2.
That opens a possibility to sharply reduce climate impact in the short term. But the researchers found that despite efforts to cut methane emissions, atmospheric concentrations of the gas are still rising.
- Rising in most countries -
An average of 6.1 million tonnes of methane were added to atmosphere per year in the 2000s.
That rose to 20.9 million tonnes per year in the 2010s. It hit 41.8 million tonnes in 2020.
"Anthropogenic (human-made) emissions have continued to increase in almost every other country in the world, with the exception of Europe and Australia, which show a slow declining trend," Global Carbon Project executive director Pep Canadell, one of the study's co-authors, told AFP.
The largest increases have come from China and southeast Asia and have been primarily linked to coal extraction, oil and gas production and landfills, the researchers found.
The La Nina weather phenomenon has also led to an increase in methane from natural sources, they said.
A drop in nitrogen oxides pollution in 2020, when use of transport plunged due to the Covid-19 pandemic, had a paradoxical impact. It is key in preventing methane from accumulating in the atmosphere.
- 'Mirage' -
Rising methane pollution is undermining efforts to keep the Earth's average temperature from rising by more than 2.0 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
A "Global Methane Pledge" was launched in 2021 by the European Union and United States to cut global methane emissions by 30 percent from 2020 levels, by the cutoff date of 2030.
More than 150 countries have signed up -- but not China, India or Russia.
"Right now, the goals of the Global Methane Pledge seem as distant as a desert oasis," said lead author of the Environmental Research Letters paper, Stanford University scientist Rob Jackson.
"We all hope they aren't a mirage."
China and the United States are preparing to host a summit on greenhouse gasses other than CO2 later this year, potentially raising the prospect of further pledges by governments.
F.Bennett--AMWN


