-
 Liverpool late show floors Nottingham Forest
Liverpool late show floors Nottingham Forest
-
Rimac Nevera R: Beyond imagination

-
 USA beat Canada to win men's Olympic ice hockey gold
USA beat Canada to win men's Olympic ice hockey gold
-
Samardzic seals comeback win for Atalanta over Napoli

-
 Eileen Gu switches slopes for catwalk after Olympic flourish
Eileen Gu switches slopes for catwalk after Olympic flourish
-
Luce: Ferrari's ingenious electric revolution

-
 Miller guides South Africa to 187-7 against India
Miller guides South Africa to 187-7 against India
-
Scotland boss 'proud' of comeback Six Nations win over Wales

-
 Iranian students rally for second day as fears of war with US mount
Iranian students rally for second day as fears of war with US mount
-
US Secret Service kills man trying to access Trump Florida estate

-
 Coventry 'let the Games do their magic': former IOC executives
Coventry 'let the Games do their magic': former IOC executives
-
Cayenne Turbo Electric 2026

-
 Sri Lanka have to qualify 'the hard way' after England drubbing
Sri Lanka have to qualify 'the hard way' after England drubbing
-
Doris says Six Nations rout of England is sparking Irish 'belief'

-
 Thousands of pilgrims visit remains of St Francis
Thousands of pilgrims visit remains of St Francis
-
Emotional Gu makes history with Olympic freeski halfpipe gold

-
 Impressive Del Toro takes statement victory in UAE
Impressive Del Toro takes statement victory in UAE
-
Gu wins triumphant gold of Milan-Cortina Olympics before ice hockey finale

-
 England rout Sri Lanka for 95 to win Super Eights opener
England rout Sri Lanka for 95 to win Super Eights opener
-
Underhill tells struggling England to maintain Six Nations 'trust' as Italy await

-
 Alfa Tonale 2026: With a new look
Alfa Tonale 2026: With a new look
-
BMW 7 Series and i7: facelift in 2026

-
 Eileen Gu makes history with Olympic freeski halfpipe gold
Eileen Gu makes history with Olympic freeski halfpipe gold
-
Eileen Gu makes history with Olympic halfpipe gold

-
 Morocco flood evacuees mark muted Ramadan away from home
Morocco flood evacuees mark muted Ramadan away from home
-
Lucid Gravity 2026: Test report

-
 Sri Lanka restrict England to 146-9 in T20 World Cup Super Eights
Sri Lanka restrict England to 146-9 in T20 World Cup Super Eights
-
West Indies wary of Zimbabwe's 'X-factor' quick Muzarabani

-
 Bentley: Visions for 2026
Bentley: Visions for 2026
-
Eileen Gu wins Olympic gold in women's freeski halfpipe

-
 First 'dispersed' Winter Olympics a success -- and snow helped
First 'dispersed' Winter Olympics a success -- and snow helped
-
Six stand-out moments from the 2026 Winter Olympics

-
 Andrew's arrest hands King Charles fresh royal crisis
Andrew's arrest hands King Charles fresh royal crisis
-
Afghans mourn villagers killed in Pakistani strikes

-
 Jeeno Thitikul brings home LPGA win in Thailand
Jeeno Thitikul brings home LPGA win in Thailand
-
Snowboard champion Karl '99 percent' sure parallel giant slalom will stay in Olympics

-
 Greenland does not need US hospital ship: Danish minister
Greenland does not need US hospital ship: Danish minister
-
Russian missile barrage hits energy, railways across Ukraine

-
 Ka Ying Rising makes Hong Kong racing history with 18th win
Ka Ying Rising makes Hong Kong racing history with 18th win
-
St Francis relics go on public show for first time in Italy

-
 Deflated Australia face tough questions after T20 World Cup flop
Deflated Australia face tough questions after T20 World Cup flop
-
Brazil's Lula urges Trump to treat all countries equally

-
 Knicks rally to down Rockets as Pistons, Spurs roll on
Knicks rally to down Rockets as Pistons, Spurs roll on
-
Brumbies end 26-year jinx with thrashing of Crusaders

-
 Pakistan launches deadly strikes in Afghanistan
Pakistan launches deadly strikes in Afghanistan
-
Son's LAFC defeats Messi and Miami in MLS season opener

-
 Korda to face Paul in all-American Delray Beach final
Korda to face Paul in all-American Delray Beach final
-
Vikings receiver Rondale Moore dies at 25

-
 Copper, a coveted metal boosting miners
Copper, a coveted metal boosting miners
-
Indigenous protesters occupy Cargill port terminal in Brazil


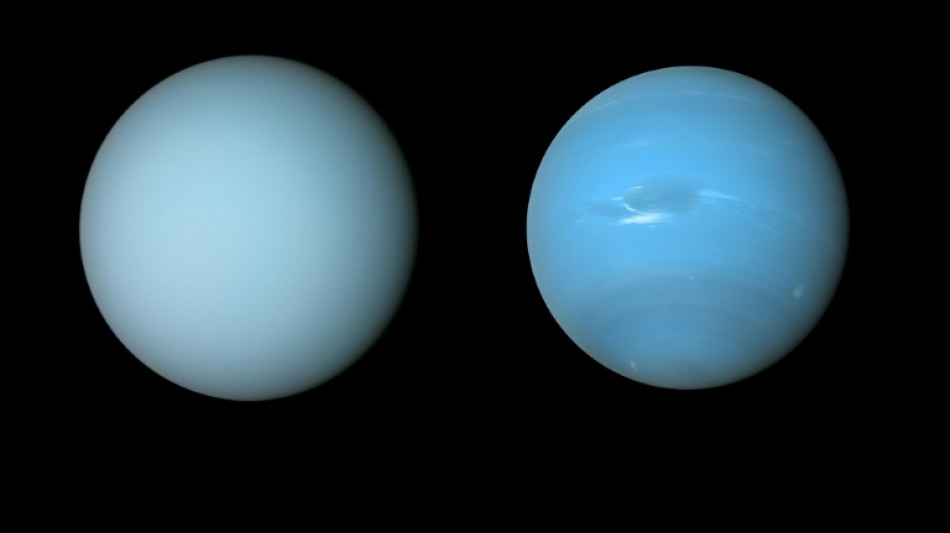
It's raining diamonds across the universe, research suggests
It could be raining diamonds on planets throughout the universe, scientists suggested Friday, after using common plastic to recreate the strange precipitation believed to form deep inside Uranus and Neptune.
Scientists had previously theorised that extremely high pressure and temperatures turn hydrogen and carbon into solid diamonds thousands of kilometres below the surface of the ice giants.
Now new research, published in Science Advances, inserted oxygen into the mix, finding that "diamond rain" could be more common than thought.
Ice giants like Neptune and Uranus are thought to be the most common form of planet outside our Solar System, which means diamond rain could be occurring across the universe.
Dominik Kraus, a physicist at Germany's HZDR research lab and one of the study's authors, said that diamond precipitation was quite different to rain on Earth.
Under the surface of the planets is believed to be a "hot, dense liquid", where the diamonds form and slowly sink down to the rocky, potentially Earth-size cores more than 10,000 kilometres (6,200 miles) below, he said.
There fallen diamonds could form vast layers that span "hundreds of kilometres or even more", Kraus told AFP.
While these diamonds might not be shiny and cut like a "a nice gem on a ring", he said they were formed via similar forces as on Earth.
Aiming to replicate the process, the research team found the necessary mix of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in a readily available source -- PET plastic, which is used for everyday food packaging and bottles.
Kraus said that while the researchers used very clean PET plastic, "in principle the experiment should work with Coca-Cola bottles".
The team then turned a high-powered optical laser on the plastic at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in California.
"Very, very short X-ray flashes of incredible brightness" allowed them to watch the process of nanodiamonds -- tiny diamonds too small to see with the naked eye -- as they formed, Kraus said.
"The oxygen that is present in large amounts on those planets really helps suck away the hydrogen atoms from the carbon, so it's actually easier for those diamonds to form," he added.
- New way to make nanodiamonds? -
The experiment could point towards a new way to produce nanodiamonds, which have a wide and increasing range of applications including drug delivery, medical censors, non-invasive surgery and quantum electronics.
"The way nanodiamonds are currently made is by taking a bunch of carbon or diamond and blowing it up with explosives," said SLAC scientist and study co-author Benjamin Ofori-Okai.
"Laser production could offer a cleaner and more easily controlled method to produce nanodiamonds," he added.
The diamond rain research remains hypothetical because little is known about Uranus and Neptune, the most distant planets in our Solar System.
Only one spacecraft -- NASA's Voyager 2 in the 1980s -- has flown past the two ice giants, and the data it sent back is still being used in research.
But a NASA group has outlined a potential new mission to the planets, possibly launching next decade.
"That would be fantastic," Kraus said.
He said he is greatly looking forward to more data -- even if it takes a decade or two.
J.Williams--AMWN


