
-
 'Girl with a Pearl Earring' to be shown in Japan, in rare trip abroad
'Girl with a Pearl Earring' to be shown in Japan, in rare trip abroad
-
Syria tells civilians to leave Aleppo's Kurdish areas

-
 'Sign of life': defence boom lifts German factory orders
'Sign of life': defence boom lifts German factory orders
-
Japan's Fast Retailing raises profit forecast after China growth

-
 Olympic champion Zheng out of Australian Open
Olympic champion Zheng out of Australian Open
-
England's Brook 'deeply sorry' for nightclub fracas

-
 New clashes in Iran as opposition urges more protests
New clashes in Iran as opposition urges more protests
-
Equity markets mostly down as traders eye US jobs data

-
 England cricket board launches immediate review into Ashes debacle
England cricket board launches immediate review into Ashes debacle
-
Dancing isn't enough: industry pushes for practical robots

-
 Asian markets mostly down as traders eye US jobs data
Asian markets mostly down as traders eye US jobs data
-
Australia to hold royal commission inquiry into Bondi Beach shooting

-
 Sabalenka accuses tour chiefs over 'insane' tennis schedule
Sabalenka accuses tour chiefs over 'insane' tennis schedule
-
Cambodia to liquidate bank founded by accused scam boss

-
 Farmers enter Paris on tractors in protest at trade deal
Farmers enter Paris on tractors in protest at trade deal
-
Viral 'Chinese Trump' wins laughs on both sides of Pacific

-
 Stokes vows to stay on but 'wrongs to put right' after crushing Ashes defeat
Stokes vows to stay on but 'wrongs to put right' after crushing Ashes defeat
-
Lidl to drop broadcast TV ads in France

-
 Stokes admits 'wrongs to put right' after crushing Ashes defeat
Stokes admits 'wrongs to put right' after crushing Ashes defeat
-
Sabalenka impresses again in Australian Open warm-up, vows more to come

-
 Gilgeous-Alexander to the rescue as Thunder sink Jazz in overtime
Gilgeous-Alexander to the rescue as Thunder sink Jazz in overtime
-
From Diaz to 'Mazadona' - five new faces starring at AFCON

-
 Startups go public in litmus test for Chinese AI
Startups go public in litmus test for Chinese AI
-
Death of Bazball: Five things we learned from Ashes series

-
 Australia's emotional Khawaja bows out for final time with Ashes win
Australia's emotional Khawaja bows out for final time with Ashes win
-
Asian markets mixed as traders eye US jobs data

-
 Australia win final Test to complete 4-1 Ashes triumph over England
Australia win final Test to complete 4-1 Ashes triumph over England
-
Trump withdraws US from key climate treaty, deepening global pullback

-
 Trump pulls US out of key climate treaty, deepening global pullback
Trump pulls US out of key climate treaty, deepening global pullback
-
Morocco under huge pressure as hosts face Cup of Nations heat

-
 Australia heatwave stokes risk of catastrophic bushfires
Australia heatwave stokes risk of catastrophic bushfires
-
Australia 71-2 at lunch, need 89 more to win final Ashes Test

-
 Study shows how fast kilos return after ending weight-loss drugs
Study shows how fast kilos return after ending weight-loss drugs
-
Trump pulls US out of key climate treaty, science body: White House

-
 England all out for 342, set Australia 160 to win final Ashes Test
England all out for 342, set Australia 160 to win final Ashes Test
-
FDA Clears Toetal Solution's Ziptoe Hammertoe System

-
 AbTherx and Red Queen Bio Partner on Therapeutic Antibody Discovery
AbTherx and Red Queen Bio Partner on Therapeutic Antibody Discovery
-
Banyan Gold Intersects Multiple High-Grade Mineralization Occurrences in Powerline and Airstrip Deposits, AurMac, Yukon, Canada

-
 Best Platform to Buy Crypto 2026 Announced
Best Platform to Buy Crypto 2026 Announced
-
New Digital Platform Fast Food Menu info Launches to Simplify Fast-Food Menu and Pricing Decisions

-
 Guam W2 Electronic Filing and EFW2 Generator for GuamTax.com W-2GU Wage Data Upload Announced by Real Business Solutions
Guam W2 Electronic Filing and EFW2 Generator for GuamTax.com W-2GU Wage Data Upload Announced by Real Business Solutions
-
Silver Range Provides an Operational Update

-
 Zenwork Joins the National Association of Computerized Tax Processors (NACTP)
Zenwork Joins the National Association of Computerized Tax Processors (NACTP)
-
Kee Ming Group Berhad Inks Underwriting Agreement With TA Securities Ahead Of ACE Market IPO

-
 Market Logic Announces Technology Partnership with Zappi to Accelerate Innovation with AI
Market Logic Announces Technology Partnership with Zappi to Accelerate Innovation with AI
-
Just - Evotec Biologics Receives Grant for AI-Driven Optimization of Monoclonal Antibody Developability for Affordable Access

-
 Lighthouse Names Georg Beyschlag Chief Financial Officer as Company Scales for Next Phase of Global Growth
Lighthouse Names Georg Beyschlag Chief Financial Officer as Company Scales for Next Phase of Global Growth
-
Storm in a tea cup for Frank as pressure mounts on Spurs boss

-
 Sesko spark masks Man Utd disappointment for Fletcher
Sesko spark masks Man Utd disappointment for Fletcher
-
Venezuelan opposition blindsided by Trump, waiting it out


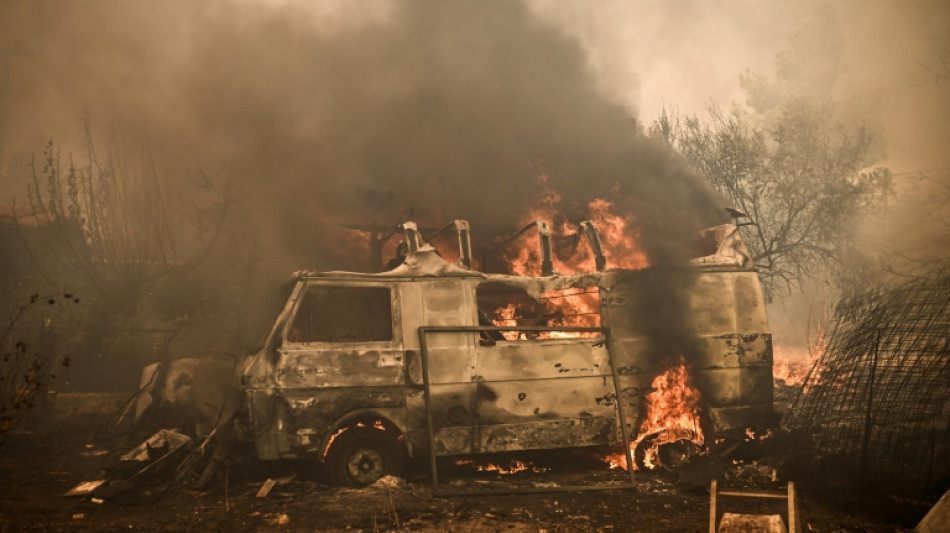
Climate change boosts risk of extreme wildfires 25%: study
Climate change has sharply boosted the risk of fast-spreading wildfires, according to a Californian study published Wednesday that offers lessons for prevention after recent disasters in Canada, Greece and Hawaii.
Scientists at the Breakthrough Institute, a non-profit research centre, found that human-caused warming increased the frequency of "extreme daily wildfire" by 25 percent on average compared to the pre-industrial era, in a study in the journal Nature.
Examining a series of blazes from 2003 to 2020, they used machine learning to analyse the link between higher average temperatures, dryer conditions and the fastest-spreading blazes -– ones that burn more than 10,000 acres (4,000 hectares) a day.
The impact of climate change varied from fire to fire.
In certain partly dry conditions, global warming pushed the area beyond key thresholds, making extreme fires much more likely. In very dry conditions, the impact was less.
"This means that we should pay the closest attention to the places and times that historically have experienced conditions just on the moist side of these thresholds, but which are being pushed over these thresholds onto the dry side by background warming," lead author Patrick Brown told AFP.
- Fierce wildfire season -
The researchers calculated that the risk could increase on average by 59 percent by the end of the century under a "low-emissions" scenario where global warming is limited to 1.8 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, and up to 172 percent in an unbridled high-emissions scenario.
Earth's surface has already warmed 1.2C.
Using data from recorded fires, the researchers measured the probability of a given blaze turning into an "extreme" one. Then they used computer models to calculate how far the post-industrial rise in temperatures had increased that risk.
The study controlled for variables such as precipitation, wind and absolute humidity and the researchers warned that changes in these could make the risk from global warming even worse.
California has suffered a string of extreme wildfires in recent years.
In 2020, more than 30 people died and four million acres were devoured by flames in some of the biggest fires in the state's history. The November 2018 "Camp Fire" killed 86 people.
The study's publication followed a summer of wildfires that killed at least 115 people in Hawaii and forced 200,000 from their homes in Canada.
Greece is battling what EU officials called the bloc's biggest wildfire on record along a 10-kilometre (six-mile) front. It has killed 20 people.
A 2022 United Nations Environment Programme report on wildfires said they are becoming more common due to hotter, dryer conditions caused by climate change, including in regions not traditionally prone to them.
- Fire prevention -
Nature study author Brown said the insights into dryness thresholds could aid prevention measures, for example by indicating the best spots for thinning and prescribed burning of vegetation to reduce the dry natural matter that wildfires feed on, known as "hazardous fuel".
"We are finding that under most conditions, the impact of hazardous fuel reductions can completely negate the impact of climate change," he said.
"It is plausible to have a future of much less wildfire danger despite climate change if we conduct these fuel treatments at scale."
He said the findings could also inform precautions regarding power lines and indicate where monitoring and awareness campaigns should be focussed, and firefighting resources deployed.
Other wildfire experts said awareness of fire risks will become increasingly important for authorities and even holidaymakers.
In a separate briefing by wildfire specialists on Wednesday not related to the study, Andrew Sullivan of Australia's national science agency CSIRO said expenditure was typically "skewed" towards responding to wildfires with not enough money allocated for preventing them.
He said there was a "global need to rebalance expenditure to improve risk mitigation" measures such as managing vegetation and fire-danger forecasting.
Y.Kobayashi--AMWN

