
-
 How AFP has used data analysis to cover the Ukraine war
How AFP has used data analysis to cover the Ukraine war
-
Paris says US envoy pledges not to 'interfere' in France affairs

-
 Iran says students must respect 'red lines' after protests
Iran says students must respect 'red lines' after protests
-
Italian biathlete Giacomel has heart surgery after Olympic withdrawal

-
 Gazans salvage ancient books in mosque library damaged by war
Gazans salvage ancient books in mosque library damaged by war
-
Farhan scores 63 as England restrict Pakistan to 164-9

-
 Stocks bounce as traders assess AI fallout, tariffs
Stocks bounce as traders assess AI fallout, tariffs
-
Brazil court tries politicians over hit on Black councilwoman

-
 Senegal PM vows to double penalty for same-sex relations
Senegal PM vows to double penalty for same-sex relations
-
UK govt backs releasing documents tied to 'rude' ex-prince Andrew

-
 Novo Nordisk to slash prices of weightloss drugs in US
Novo Nordisk to slash prices of weightloss drugs in US
-
Welllage says Sri Lanka can rescue T20 World Cup campaign

-
 UK's royal protection officers urged to speak up in Epstein probe
UK's royal protection officers urged to speak up in Epstein probe
-
Aid groups petition Israel's top court to halt ban on Gaza, West Bank ops

-
 UEFA can make fight against racism more than a slogan: Real Madrid's Arbeloa
UEFA can make fight against racism more than a slogan: Real Madrid's Arbeloa
-
Bali flooding prompts tourist evacuation: official

-
 Jones says Borthwick's 'title-decider' comments behind England collapse
Jones says Borthwick's 'title-decider' comments behind England collapse
-
UK fines Reddit nearly $20 mn over children's data failures

-
 PSG star Hakimi faces trial for alleged rape
PSG star Hakimi faces trial for alleged rape
-
Netflix, Prime and Disney+ face UK broadcasting regulation

-
 Greece set new tourism record in 2025
Greece set new tourism record in 2025
-
Zelensky says Ukraine unbroken after 4 years, but Russia vows to fight on

-
 Zelenksy says Ukraine unbroken after 4 years, but Russia vows to fight on
Zelenksy says Ukraine unbroken after 4 years, but Russia vows to fight on
-
Snoop Dogg 'can't wait' for first Swansea visit

-
 Stocks fluctuate as traders assess AI fallout, tariffs
Stocks fluctuate as traders assess AI fallout, tariffs
-
Post-it maker 3M faces Belgian trial over 'forever' chemicals

-
 UK comedian Russell Brand pleads not guilty to new rape, assault charges
UK comedian Russell Brand pleads not guilty to new rape, assault charges
-
Duterte drew up 'death lists', boasted about murders: ICC prosecutor

-
 UK govt urged to release documents linked to ex-prince Andrew
UK govt urged to release documents linked to ex-prince Andrew
-
Rights group slams treatment of viral Japanese monkey

-
 Inside the bunker where Zelensky led response to Russian invasion
Inside the bunker where Zelensky led response to Russian invasion
-
France demands explanation from US envoy over 'surprise' no-show

-
 Putin failed to achieve goals in Ukraine, Zelensky says on war anniversary
Putin failed to achieve goals in Ukraine, Zelensky says on war anniversary
-
China tightens Japanese trade restrictions as spat worsens

-
 Ukraine war exhibition opens at Berlin Nazi bunker museum
Ukraine war exhibition opens at Berlin Nazi bunker museum
-
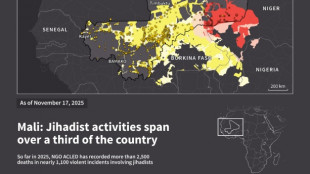
Jihadist threat puts eastern Senegal on edge
-
 Kim Yo Jong: the powerful sister behind North Korea's supreme leader
Kim Yo Jong: the powerful sister behind North Korea's supreme leader
-
North Korea ruling party promotes Kim Jong Un's younger sister

-
 Mexico's Jalisco cautiously tries returning to normal after cartel violence
Mexico's Jalisco cautiously tries returning to normal after cartel violence
-
Mexico's violence-hit Guadalajara to host World Cup games

-
 Mourinho's Bernabeu homecoming upended by suspension, racism row
Mourinho's Bernabeu homecoming upended by suspension, racism row
-
China targets Japanese companies over military ties

-
 Griezmann in talks to join MLS side Orlando City: source
Griezmann in talks to join MLS side Orlando City: source
-
France to revoke US envoy's govt access after summons no-show

-
 Spurs overpower Pistons in clash of NBA's form teams
Spurs overpower Pistons in clash of NBA's form teams
-
Inoue to fight Nakatani in Tokyo in May: reports

-
 Canada PM to push trade, rebuild fractured ties in India trip
Canada PM to push trade, rebuild fractured ties in India trip
-
Asian markets mixed as traders weigh AI and tariffs outlook

-
 Votes may 'melt like snow': Reform, Greens eye Labour UK bastion
Votes may 'melt like snow': Reform, Greens eye Labour UK bastion
-
Venezuela says exiles welcome to return following mass amnesty


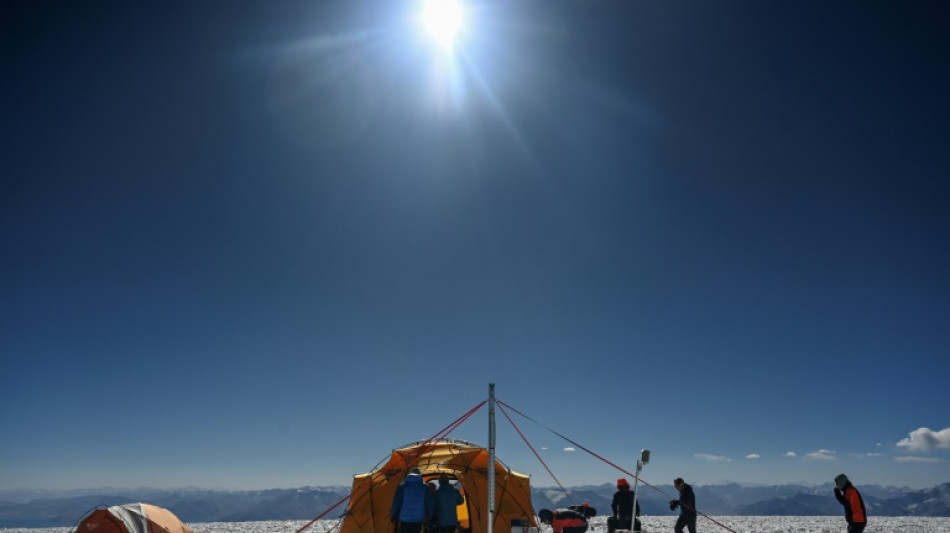
Scientists probe Tajik glacier for clues to climate resistance
Greenland is melting, the Alps are melting and the Himalayas are melting -- yet in one vast mountain region, huge glaciers have remained stable, or even gained mass, in recent decades. Can it last?
To find out, a dozen scientists, accompanied exclusively by an AFP photographer, trekked high over one glacier in eastern Tajikistan to drill for ice cores -- ancient, deep samples that can shed precious light on climate change.
In September and October, they first spent four days crossing the country from west to east in four-wheel drives, then climbed on foot to over 5,800 metres altitude on the Kon-Chukurbashi ice cap, near the Chinese border.
Camping for a week at the summit, in freezing temperatures and despite a day-long blizzard, the scientists from Switzerland, Japan, the United States and Tajikistan drilled the glacier to extract two 105-metre-long ice cores, in sections.
These layers of ice, compacted over centuries, perhaps millennia, form an archive of climate indicators, yielding data on past snowfall, temperatures, atmosphere and dust.
They must now be analysed in a laboratory to reveal their dates, said the leader of the team, Evan Miles, a glaciologist affiliated with the universities of Fribourg and Zurich.
"We're hopeful for a truly unique core, not just for the region, but for the broader region actually, probably extending back 20 to 25 or 30,000 years."
- Glacier temperature anomaly -
The apparently resistant glaciers are spread over thousands of kilometres of high mountain ranges in Central Asia, including Karakoram, Tian Shan, Kun Lun and the Pamir mountains of Tajikistan.
By delving back in time in the ice there, researchers hope to find out why these glaciers have resisted the general planetary warming of recent decades -- and whether this so-called "Karakoram anomaly" could be ending.
"This whole region is globally unique because over the last 25 years, these glaciers have shown very, very limited mass loss and even mass gain," said Miles.
The glaciers have shown some limited signs of loss in recent years, but scientists want to determine whether this is a natural variation or the beginning of a real decline.
"In order to understand that, we really, really need to have a longer time period of records of both temperature and precipitation at the glacier sites," said Miles.
"That's the type of information that an ice core can tell us."
- Glacier climate analysis -
One core will be sent to Japan for analysis and another stored in an underground sanctuary in Antarctica at minus 50C.
That naturally cold storage site is a project of the Ice Memory Foundation, which supported the Tajikistan expedition along with main funder, the Swiss Polar Institute.
The foundation, created in 2021 by French, Italian and Swiss universities and research centres, has already collected several cores in the Alps, Greenland, the Andes and elsewhere.
Future scientists will "be able to analyse (them) with their most modern analytical tools in 50, 100, 200 years and extract new information", said Ice Memory's president Thomas Stocker.
"We will probably lose 90 percent of our glacier mass on the Earth," Stocker told AFP. "So we are trying to help preserve a thing that is threatened by human action."
The scientists were scheduled to review their mission during a news conference in the Tajik capital Dushanbe on Monday.
F.Bennett--AMWN



