
-
 Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris
Top US, China economy officials to meet for talks in Paris
-
Israel strikes Beirut after threatening to expand Lebanon operations

-
 Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise
Out with a bang: Morrissey cancels Spain concert over noise
-
Vingegaard soloes to victory in Paris-Nice fifth stage

-
 Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia
Poland reels from row over EU loans to fend off Russia
-
Spurs extend season ticket deadline as relegation fears grow

-
 Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military
Laundry fire on giant US aircraft carrier injures two: US military
-
Mauritanian anti-slavery stalwart Boubacar Ould Messaoud dead

-
 Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub
Behind Cambodian border casino, Thai military shows off a scam hub
-
Chile's Smiljan Radic Clarke wins Pritzker architecture prize

-
 Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'
Scotland boss Townsend says Six Nations title 'out of our hands'
-
Sheehan and van der Flier recalled for Triple Crown decider with Scots

-
 Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy
Chelsea's Neto faces UEFA punishment for pushing ball boy
-
Engraved tombs help keep memories alive in Pakistan

-
 IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred
IPL-linked Sunrisers sign Pakistan's Ahmed for Hundred
-
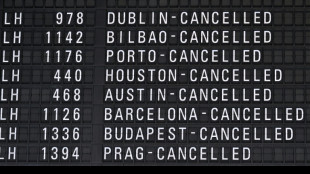
Lufthansa flights axed as pilots walk out
-
 Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister
Turkey talking to US, Iran in bid to end war: minister
-
Oil tops $100 as fresh Iran attacks offset stockpiles release

-
 Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages
Fears grow for French loans at Louvre Abu Dhabi as war rages
-
US military 'not ready' to escort tankers through Hormuz Strait: energy secretary

-
 'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel
'One war too many': Lebanese angry with Hezbollah for attacking Israel
-
Scotland make three changes for crucial Six Nations clash against Ireland

-
 Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack
Russia jails 15 for life over IS-claimed 2024 concert hall attack
-
WWII leader Churchill to be removed from UK banknotes

-
 EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US
EU vows to 'respond firmly' to any trade pact breach by US
-
The rain in Spain was worst in nearly 50 years

-
 'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform
'Punished' for university: debt-laden UK graduates urge reform
-
Mideast war to brake German recovery: institute

-
 More than goals: Valverde draws Real Madrid map to glory
More than goals: Valverde draws Real Madrid map to glory
-
Tandy urges Wales to raise level in Six Nations clash against Italy

-
 Mideast oil shock 'largest' in history as Iran hits new Gulf targets
Mideast oil shock 'largest' in history as Iran hits new Gulf targets
-
France coach Galthie beefs up his second row for England 'Crunch'

-
 China-North Korea train arrives in Pyongyang after 6-year halt
China-North Korea train arrives in Pyongyang after 6-year halt
-
Noma co-founder quits after abuse allegations

-
 China's leaders project stability despite Middle East war
China's leaders project stability despite Middle East war
-
Lebanon says Israeli strike on Beirut seafront kills 8

-
 Wales unchanged for Italy Six Nations finale
Wales unchanged for Italy Six Nations finale
-
Back to work for Bangladesh migrants as Mideast war grinds on

-
 Russia jails 15 for life over 2024 concert hall attack
Russia jails 15 for life over 2024 concert hall attack
-
'Hurt' Atalanta try to bounce back from Bayern battering at Serie A leaders Inter

-
 Businessman or politician? Billionaire Czech PM under fire again
Businessman or politician? Billionaire Czech PM under fire again
-
Mideast war lands India restaurants in soup

-
 Lost page of legendary Archimedes palimpsest found in France
Lost page of legendary Archimedes palimpsest found in France
-
World champion Norris says McLaren must 'improve in all areas'

-
 Early F1 leader Russell says 'championship means nothing at this point'
Early F1 leader Russell says 'championship means nothing at this point'
-
Ferrari's Leclerc hopes year of the horse a good omen in China

-
 Cathay Pacific roughly doubles fuel surcharge on most routes
Cathay Pacific roughly doubles fuel surcharge on most routes
-
BMW profit holds up despite Trump tariffs, China woes

-
 Electric vehicle rethink to cost Honda almost $16 billion
Electric vehicle rethink to cost Honda almost $16 billion
-
Bangladesh parliament reconvenes after uprising and polls


Scientists explain why peanuts 'dance' when dropped in beer
When peanuts are dropped into a pint of beer, they initially sink to the bottom before floating up and "dancing" in the glass.
Scientists have dug deep seeking to investigate this phenomenon in a new study published on Wednesday, saying it has implications for understanding mineral extraction or bubbling magma in the Earth's crust.
Brazilian researcher Luiz Pereira, the study's lead author, told AFP that he first had the idea when passing through Argentina's capital Buenos Aires to learn Spanish.
It was a "bartender thing" in the city to take a few peanuts and pop them into beers, Pereira said.
Because the peanuts are denser than the beer, they first sink down to the bottom of the glass.
Then each peanut becomes what is called a "nucleation site". Hundreds of tiny bubbles of carbon dioxide form on their surface, acting as buoys to drag them upwards.
"The bubbles prefer to form on the peanuts rather than on the glass walls," explained Pereira, a researcher at Germany's Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
When the bubbles reach the surface, they burst.
The peanuts then dive down before being propelled up again by freshly formed bubbles, in a dance that continues until the carbon dioxide runs out -- or someone interrupts by drinking the beer.
In a series of experiments, the team of researchers in Germany, Britain and France examined how roasted, shelled peanuts fared in a lager-style beer.
- Next up: more beers -
The study, published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, describes two key factors in what the researchers dubbed the "beer–gas–peanut system".
They found that the larger the "contact angle" between the curve of an individual bubble and the surface of the peanut was, the more likely it was to form and grow.
But it cannot grow too much -- a radius of under 1.3 millimetres is ideal, the study said.
Pereira said he hoped that "by deeply researching this simple system, which everyone can grasp, we can understand a system" that would be useful for industry or explaining natural phenomena.
For example, he said the floatation process was similar to the one used to separate iron from ore.
Air is injected, in a controlled way, into a mixture in which a mineral -- such as iron -- "will rise because bubbles attach themselves more easily to it, while other (minerals) sink to the bottom," he said.
The same process could also explain why volcanologists find that the mineral magnetite rises to higher layers in the crystallised magma of the Earth's crust than would be expected.
Like peanuts, magnetite is denser, so should sit at the bottom. But due to a high contact angle, the researchers theorise, the mineral rises through the magma with help from gas bubbles.
Of course, science is never settled -- particularly when beer is involved.
Hoping to create a better model of the dancing peanut phenomenon, Pereira said the scientists will continue to "play with the characteristics of different peanuts and different beers".
Ch.Havering--AMWN


